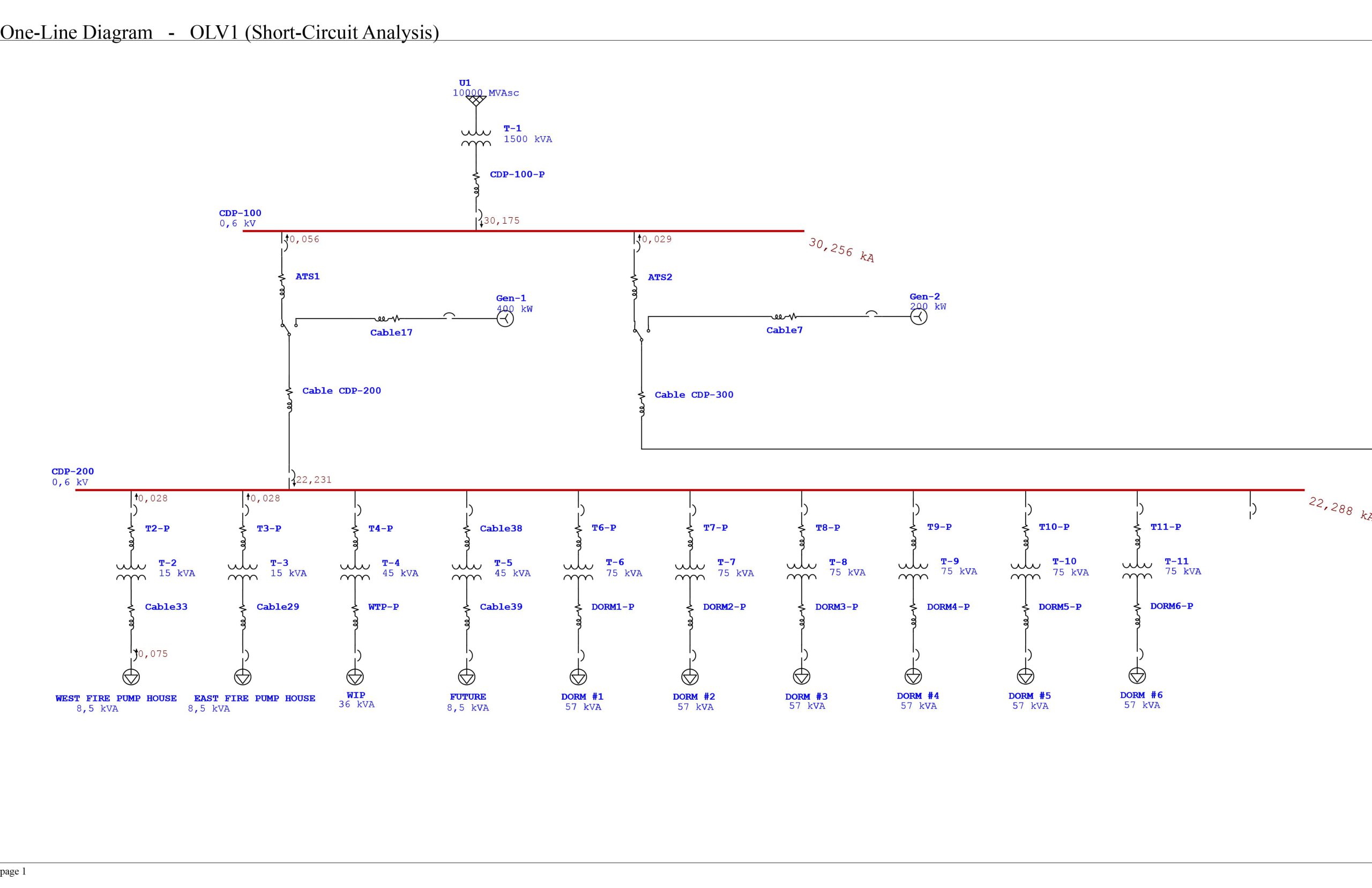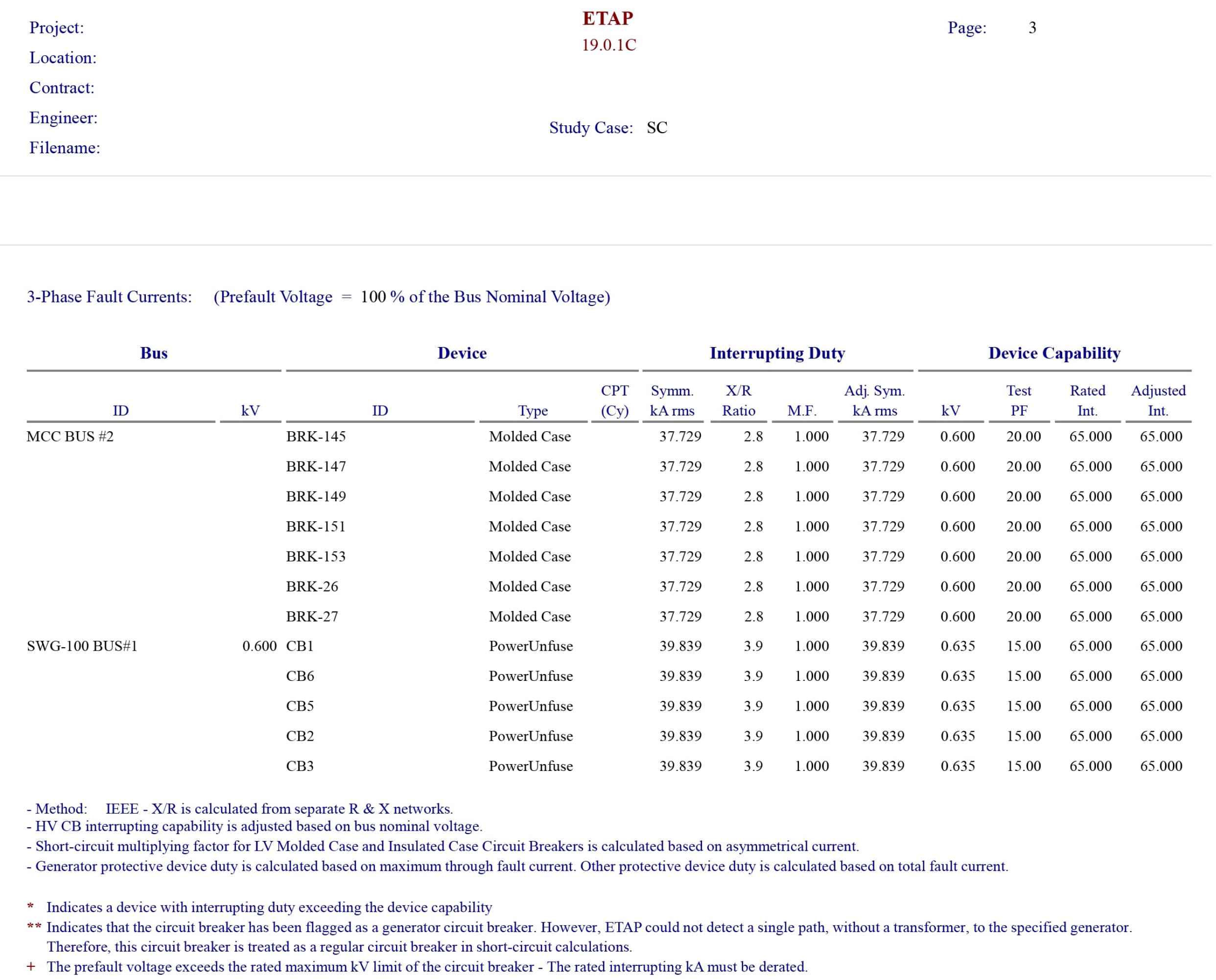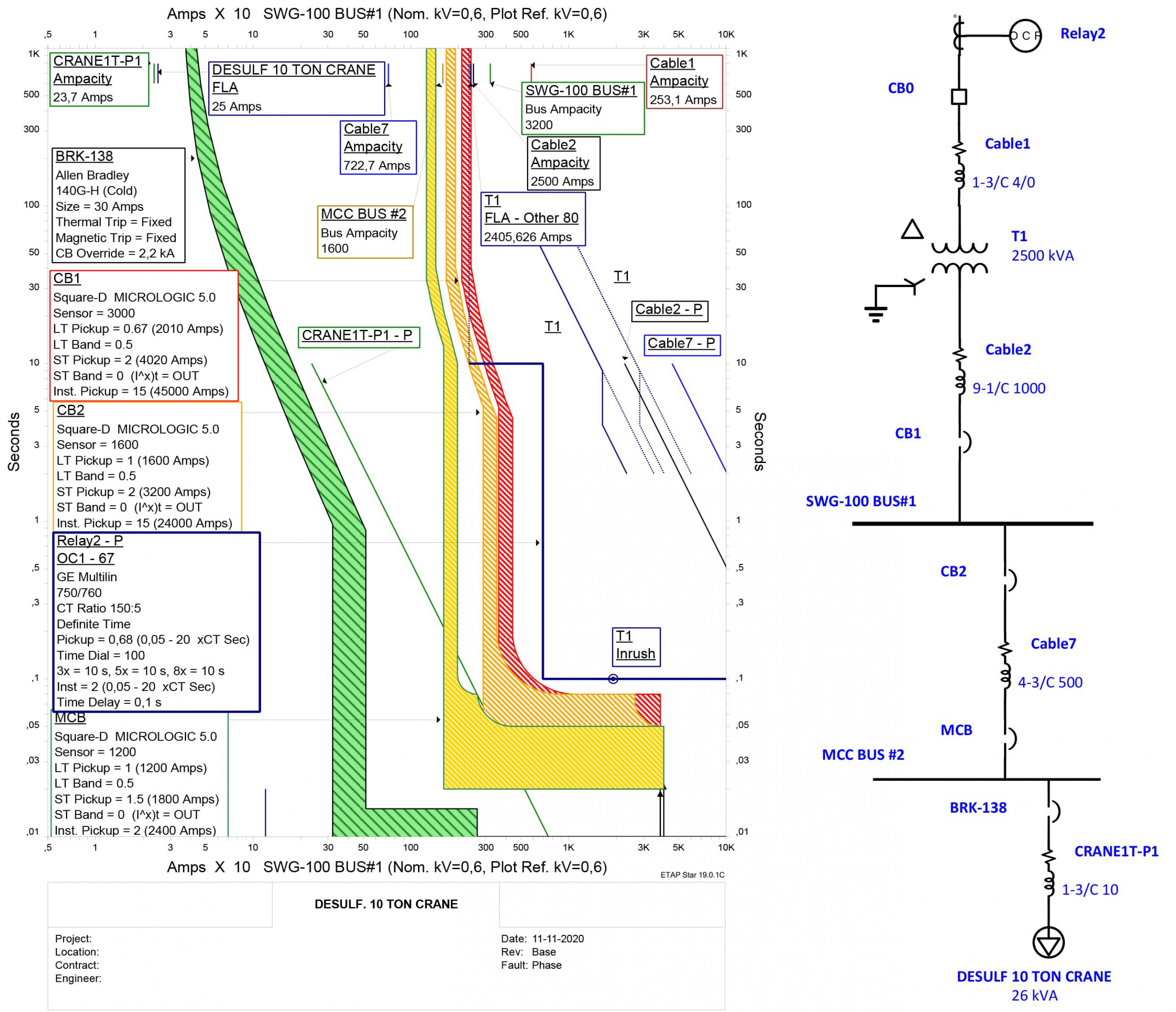
Protective Device Coordination Study
The coordination study determines the extent of overcurrent protective device coordination within an electrical system and provides an analysis of all possible operating scenarios which will be or have been influenced by the proposed additions or changes to the power distribution system. Good selectivity provides optimum protection of electrical distribution systems when fault conditions such as overloads, short circuits, arc flash, earth faults etc. occur.
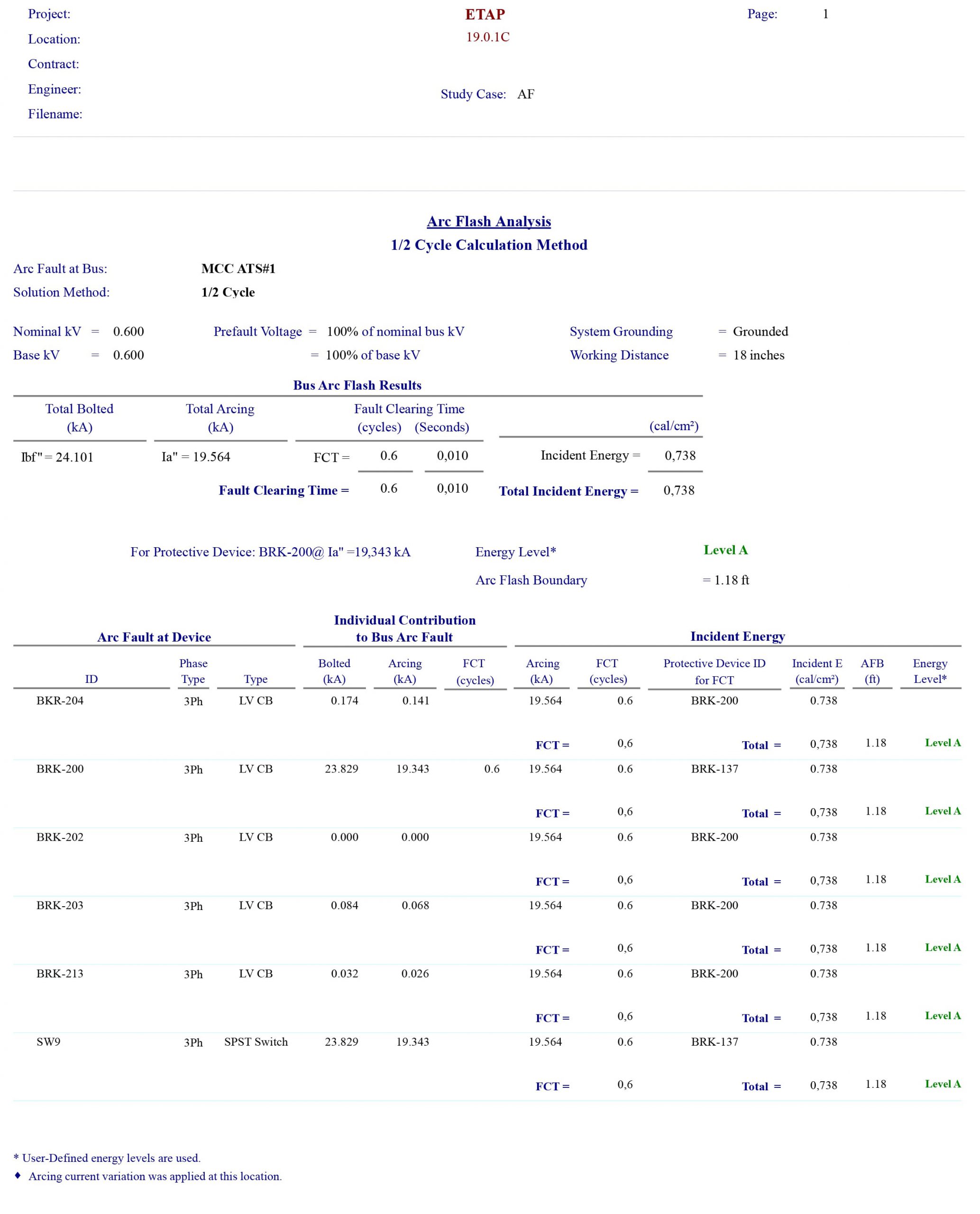
Arc-Flash Hazard Analysis
The purpose of the arc-flash analysis is to determine the arc-flash incident energy levels and flash-protection boundary distances of electrical equipment based on results found in short-circuit and coordination studies. The analysis is performed under worst-case arc-flash conditions for all modes of operation and provides an analysis of all possible operating scenarios which will be, or have been influenced by, the proposed or completed additions to the subject system.
Short circuit and coordination studies are performed to determine the available energy of an electrical system and the expected clearing time of protective devices, whereas the arc-flash hazard analysis determines the arc flash boundary and calculates the incident energy at each fault location at the prescribed working distance. Based on this information, the arc-flash hazard PPE category for the calculated incident energy level can be specified along with the arc flash boundary at each fault location.


Descriptions of the scenarios evaluated and identification of the scenario used to develop incident-energy levels are included in the study report. Any potential system operating modes including tie-breaker positions, and parallel generation are also identified within the arc-flash hazard analysis as these conditions will have an effect on the available incident energy.
Arc Flash Labels identify potential hazards with energized switch boards, panel boards, control panels and much more. Standard arc flash labels are available with either “Warning” or “Danger” headers. Write-on labels are also available. Arc Flash labels indicate the equipment-specific hazard information. These labels meet all current OSHA, NFPA, NEC and NFPA 70E requirements.
Power system studies are essential tools in understanding the expected performance of an electrical system and determining the severity of a fault or other unexpected event.
There are many different types of power system studies, each with their own special purpose and calculation method. Each analysis is unique to a particular power system, any changes within the system can affect the results of the analysis and requires recalculation.
The following types of power system study are the most common studies Engineering Solutions produce:
- Load flow study
- Short circuit calculation
- Protective device coordination study
- Arc-flash hazard analysis
Load Flow Study
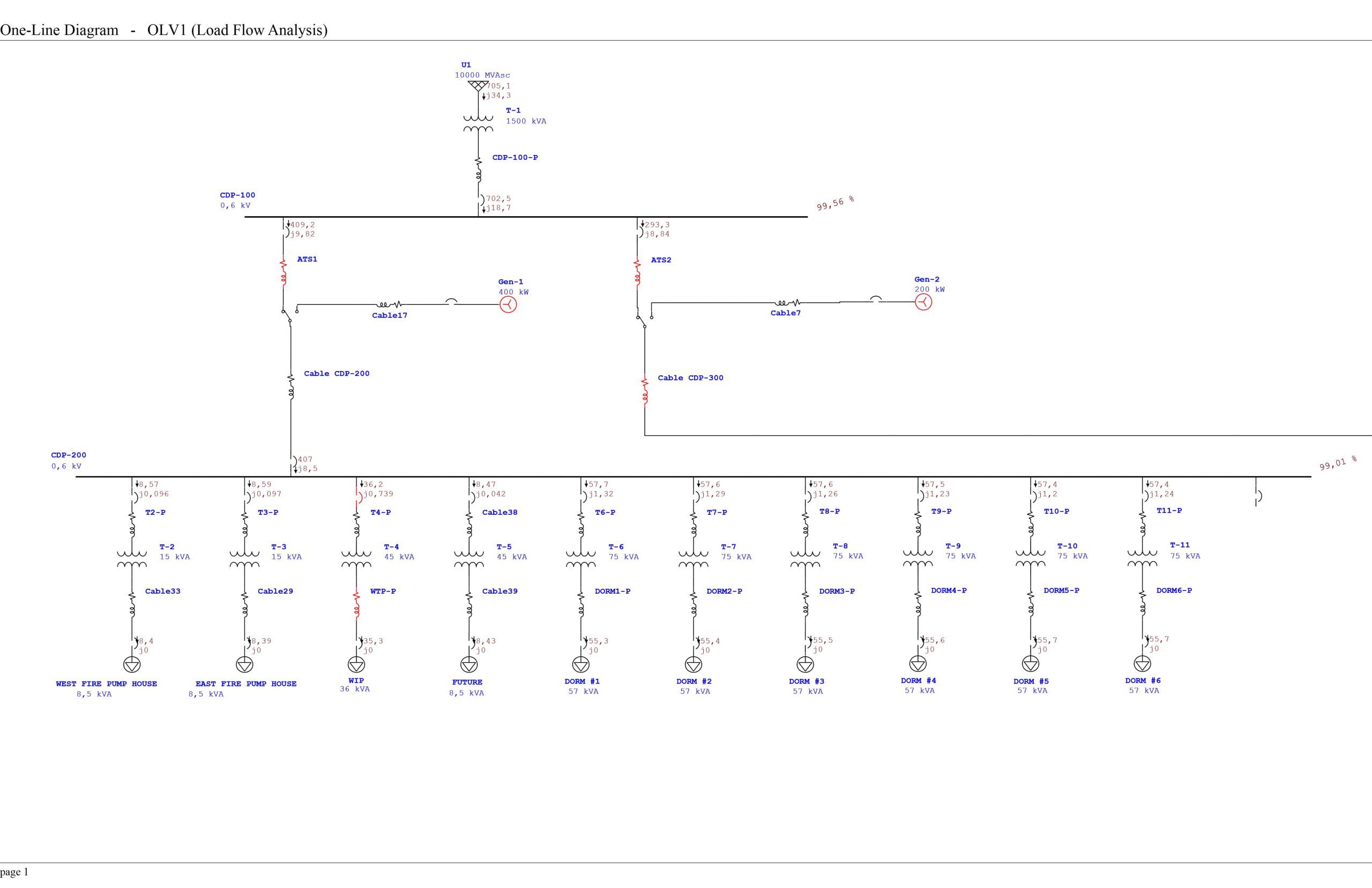
A load flow study determines the active and reactive power, voltage, current, and power factor throughout an electrical system. Load flow studies provide an analysis of all possible operating scenarios and identifies overloaded equipment.
Included within the load flow study is a tabulation of the data used to model the system components and a corresponding one-line diagram. Descriptions of the scenarios evaluated and the basis for each are also found within the study, along with:
- Tabulations of power and current flow versus equipment ratings – Identifies the percentage of rated load and the scenario for which the percentage is based, noting any overloaded quipment within the system.
- Tabulations of system voltages versus equipment ratings – Identifies the percentage of rated voltage and the scenario for which the percentage is based, noting voltage levels that fall outside the ranges recommended by equipment manufacturers.
- Tabulations of system real and reactive power losses, noting areas of concern along with conclusions and recommendations from the engineer performing the study.
Short Circuit Calculation
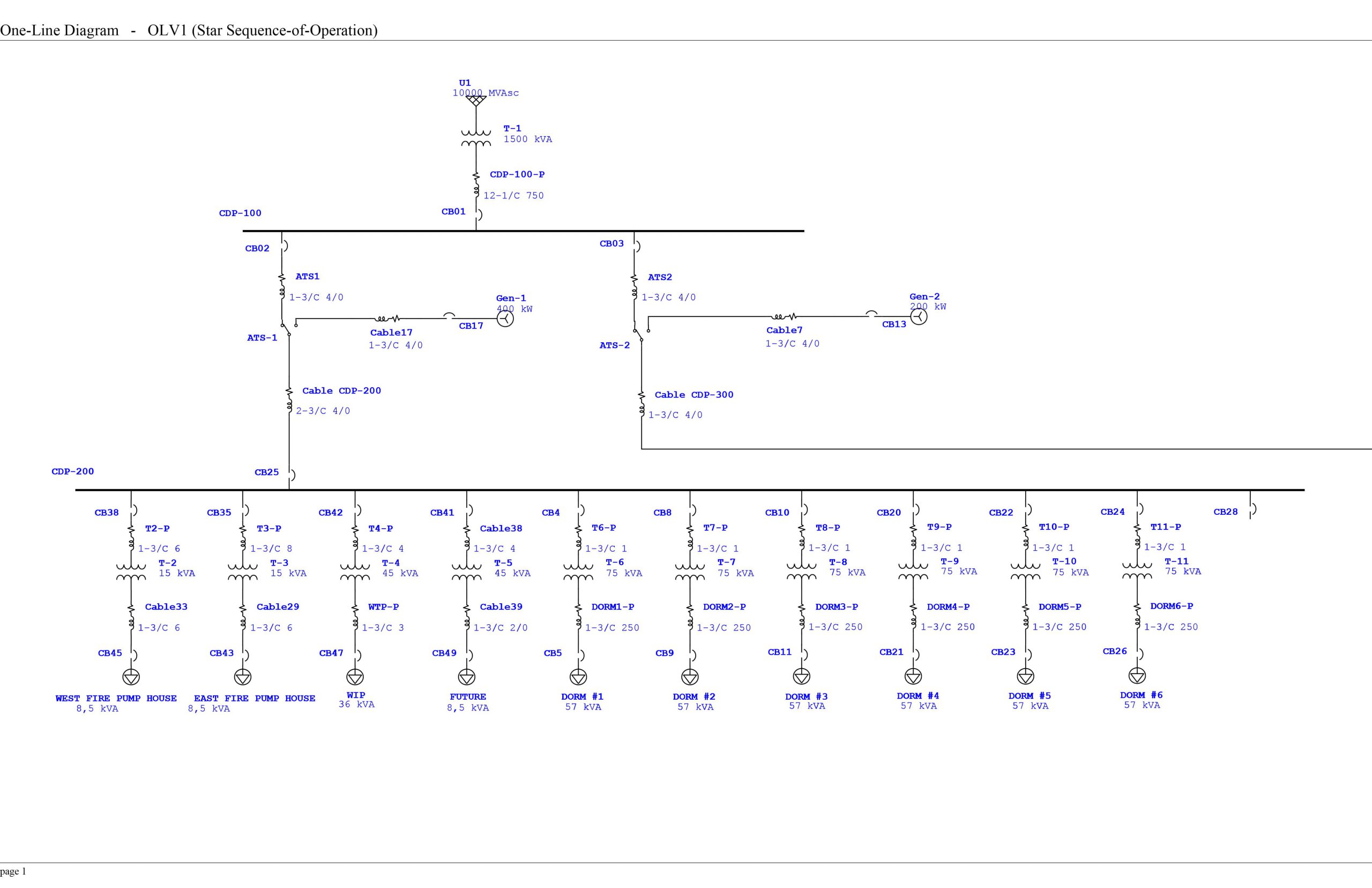
The purpose of the short circuit study is to determine the ability of each component within an electrical system to withstand and/or interrupt the system current. Short circuit studies provide an analysis of all possible operating scenarios, which will be influenced by the proposed additions or changes to the power distribution system.
Information contained within the study include tabulations of the data used to model the system components and a corresponding one-line diagram. Descriptions of the scenarios evaluated, and identification of the scenario used to evaluate equipment short-circuit current ratings are also included in the study.
Tabulations of equipment short-circuit current ratings versus available fault duties can be found in short circuit studies. The study report should clearly identify which equipment have insufficient ratings.